What did it mean to be bought, sold, and sexually exploited in the ancient world? In this powerful episode of Two Friends Talk History, Zofia is joined by doctoral candidate Florence Felsheim to explore the hidden realities of sexual trafficking in ancient Greece and Rome. Drawing on literary texts, archaeological evidence, and cognitive science, Florence unpacks how systems of enslavement and exploitation operated in societies often romanticized in popular culture.
We examine the scale of the ancient slave trade, the gendered dimensions of exploitation, and how enslaved women were commodified—expected to provide not just labor, but sexual access. From Roman brothels to banquet halls, the episode reveals how normalized sexual violence was embedded in the fabric of ancient daily life.
As part of Sexual Violence Awareness Month, this conversation sheds light on uncomfortable histories, connecting past systems of abuse to present-day conversations on power, consent, and human dignity. Listener discretion is advised.

Invisible Chains: Human Trafficking in Antiquity with Florence Felsheim – Two Friends Talk History
Human Trafficking in the Ancient World: A Forgotten Reality
When most people think of human trafficking, they imagine a modern crisis. However, the practice of exploiting people for labor, sex, and servitude dates back thousands of years. In the ancient world, trafficking was not only common—it was institutionalized and deeply woven into the fabric of many societies.
In ancient Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, and Rome, slavery was a cornerstone of the economy. Prisoners of war, kidnapped foreigners, and even impoverished citizens were often sold into slavery. Unlike modern trafficking, which is largely illegal and hidden, ancient systems openly supported human trade. Markets for slaves were publicly established and legal codes could regulate their trade and treatment.
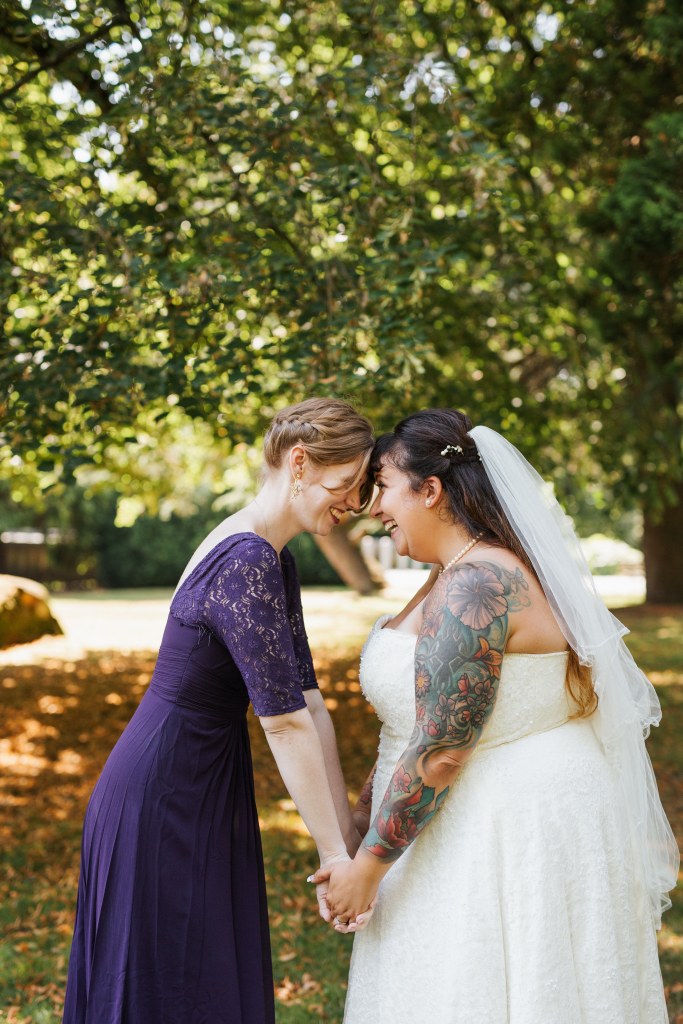
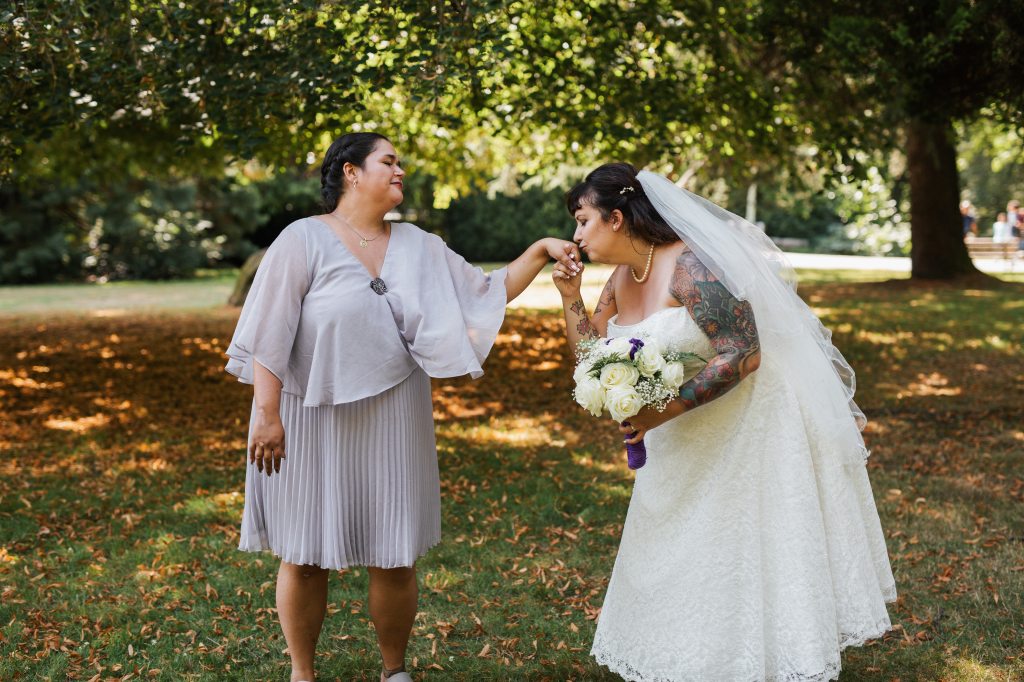
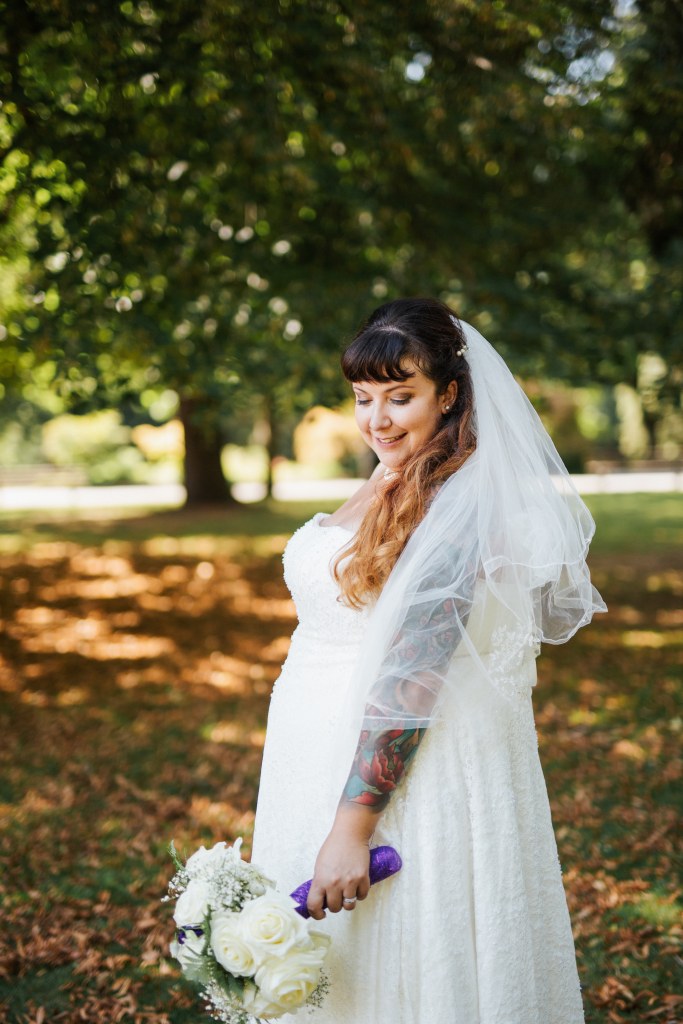
Women and children were particularly vulnerable. Many were trafficked for domestic service, labor, alongside sexual exploitation. In ancient Greece, for instance, women were commonly sold into brothels or forced to work as concubines. Rome’s vast empire relied heavily on enslaved people, many of whom were captured from conquered territories and transported long distances.
Though the term “human trafficking” didn’t exist in antiquity, the mechanisms of coercion, transport, and exploitation mirror modern patterns. Individuals lost autonomy, families were torn apart, and countless lives were shaped by violence and subjugation.
Understanding the ancient roots of human trafficking challenges the myth that it’s a purely modern problem. Instead, it reveals a tragic continuity in human history: the persistent commodification of people. While laws and attitudes have evolved, the underlying injustice remains disturbingly familiar.
By studying trafficking in the ancient world, we can better understand the cultural, economic, and political forces that continue to allow it today. Acknowledging its history is a step toward dismantling it in the present.
Speaking Through Objects

Moregine bracelet, illustrated by Zofia Guertin.
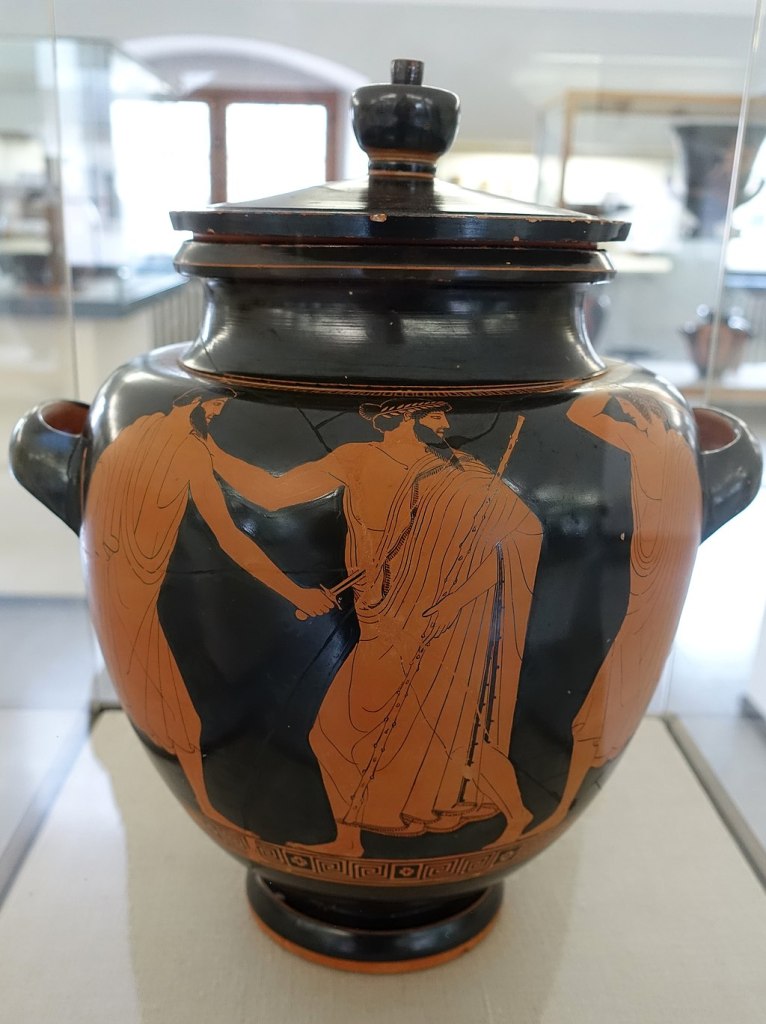
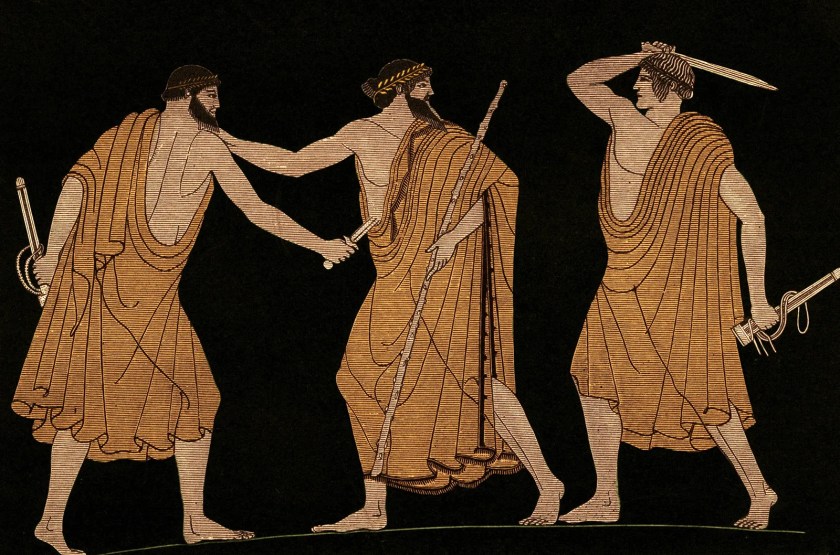
In 2000, archaeologists at Moregine, near Pompeii, uncovered a gold snake-shaped bracelet inscribed “dominus ancillae suae” (“the master to his very own slave girl”) on the body of a woman fleeing the eruption of Vesuvius. Found alongside other jewelry and coins, the bracelet, weighing about 500 grams, is crafted to coil three times around the arm. Its inscription has sparked debate: it may have been a gift to a domestic slave, a freedwoman, or a slave prostitute, or a metaphorical gift between lovers. The discovery highlights complex social dynamics and the harsh realities of slavery in ancient Roman society.
Resources
- Levin-Richardson, Sarah. “Modern Tourists, Ancient Sexualities.” Pompeii in the Public Imagination from Its Rediscovery to Today. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011.
- Keuls, Eva C. Reign of the Phallus : Sexual Politics in Ancient Athens. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1994.
- McClure, Laura. Phryne of Thespiae : Courtesan, Muse, and Myth. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2024.
- Funke, Melissa. Phryne : a life in fragments. London : Bloomsbury Academic
🌍 Sexual Violence Support Resources
If you or someone you know needs support, here are trusted organizations offering help across the globe:
1. RAINN (USA/global support)
🔗 rainn.org
📞 1-800-656-HOPE (4673)
💬 24/7 online chat
2. UN Women – End Violence Against Women
🔗 unwomen.org
3. The Survivors Trust (UK)
🔗 thesurvivorstrust.org
📧 info@thesurvivorstrust.org
4. Women Against Violence Europe (WAVE Network)
🔗 wave-network.org
5. Child Helpline International (for youth/caregivers)
🔗 childhelplineinternational.org
6. UNFPA – Global Helpline Directory
🔗 Global helpline list
7. Amnesty International – Gender & Sexuality Support
🔗 amnesty.org
💻 Online & Anonymous Support
8. Lifeline Chat (24/7, anonymous)
🔗 suicidepreventionlifeline.org/chat
🔐 Tip: Use a VPN or private browser if privacy is a concern. Always contact local emergency services if in immediate danger.
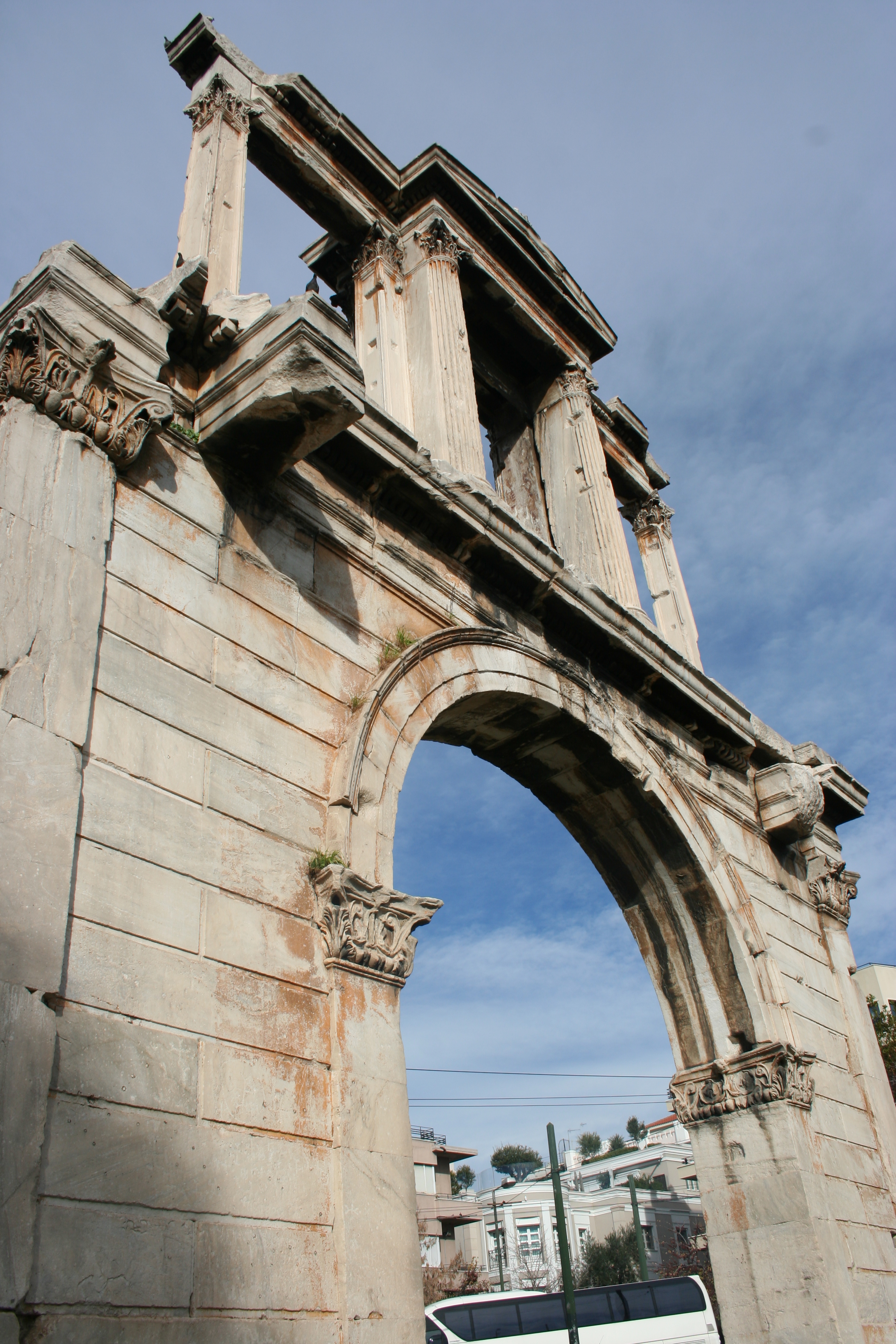







































































































 Situated next to the Olympeion, the Arch of Hadrian has quite a few stylistically complex elements and details which are exemplary of Athenian architecture done in a Roman-style. Created from solid Pentelic marble, Corinthian capitals atop pilasters among other features, are representative of architectural imagery in Roman wall painting. There were sculptures in the central niche, it has been suggested, which were of Hadrian and Theseus. This is not such an odd paring when you consider the inscriptions.
Situated next to the Olympeion, the Arch of Hadrian has quite a few stylistically complex elements and details which are exemplary of Athenian architecture done in a Roman-style. Created from solid Pentelic marble, Corinthian capitals atop pilasters among other features, are representative of architectural imagery in Roman wall painting. There were sculptures in the central niche, it has been suggested, which were of Hadrian and Theseus. This is not such an odd paring when you consider the inscriptions.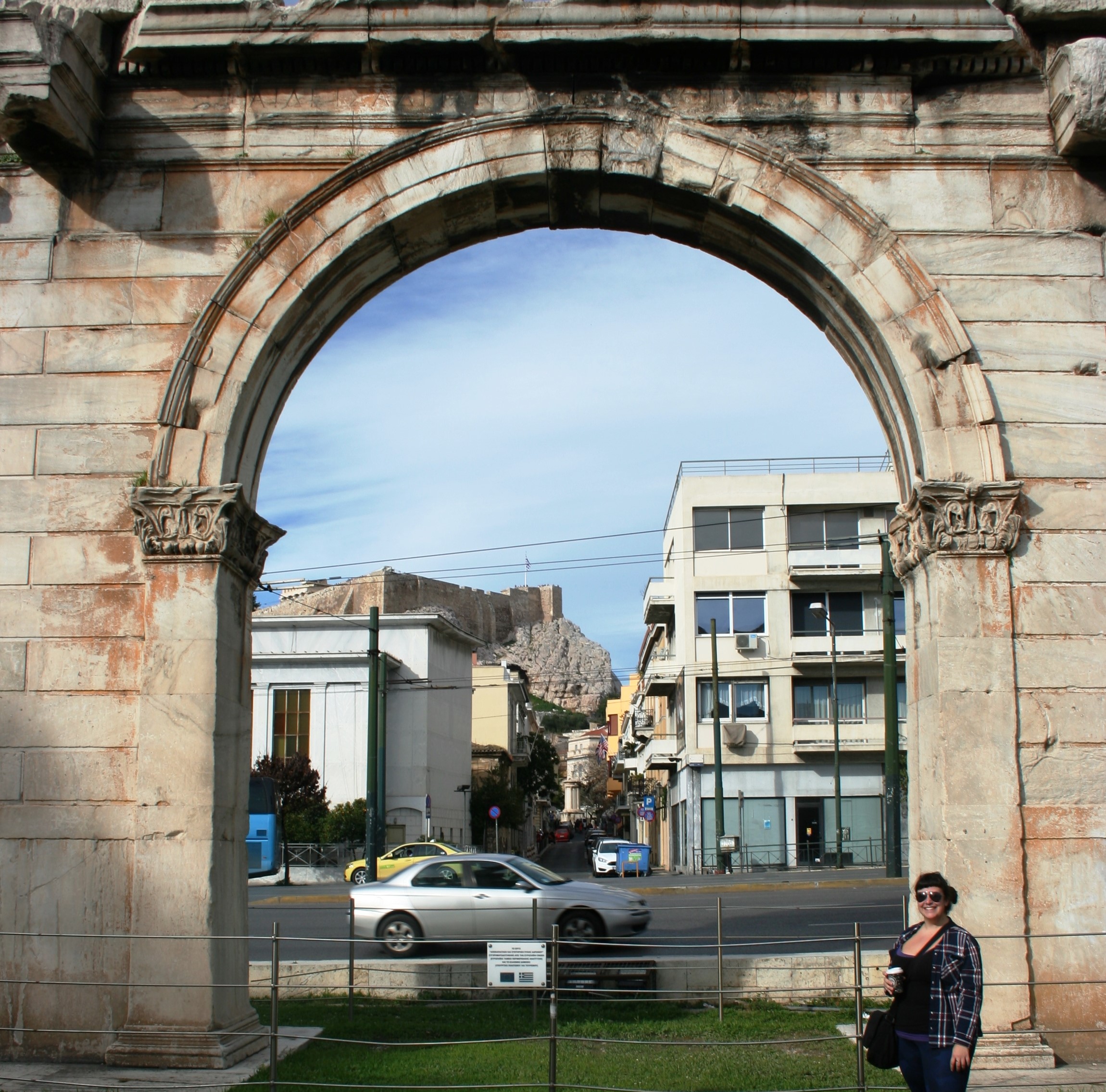 
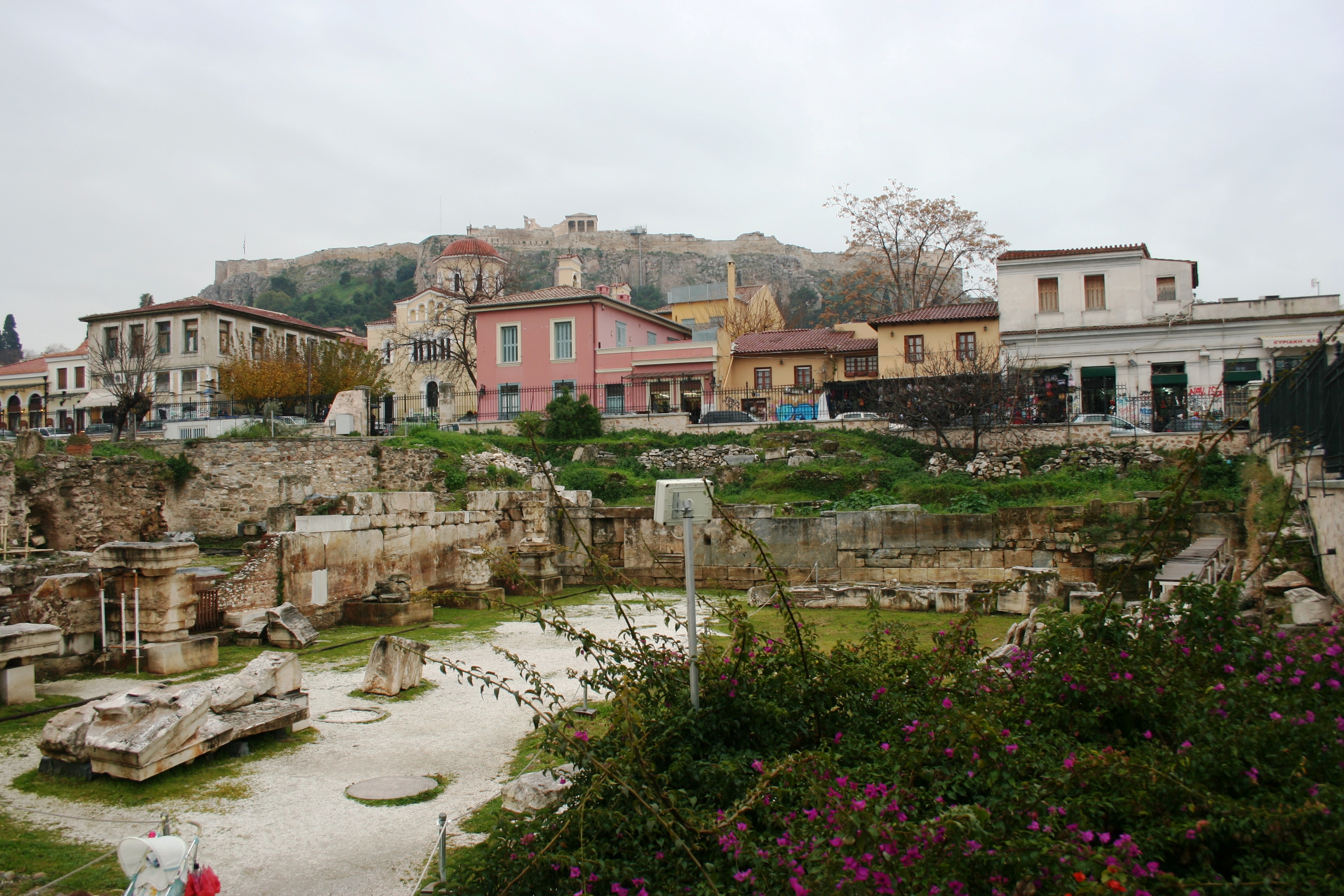 Hadrian’s Library
Hadrian’s Library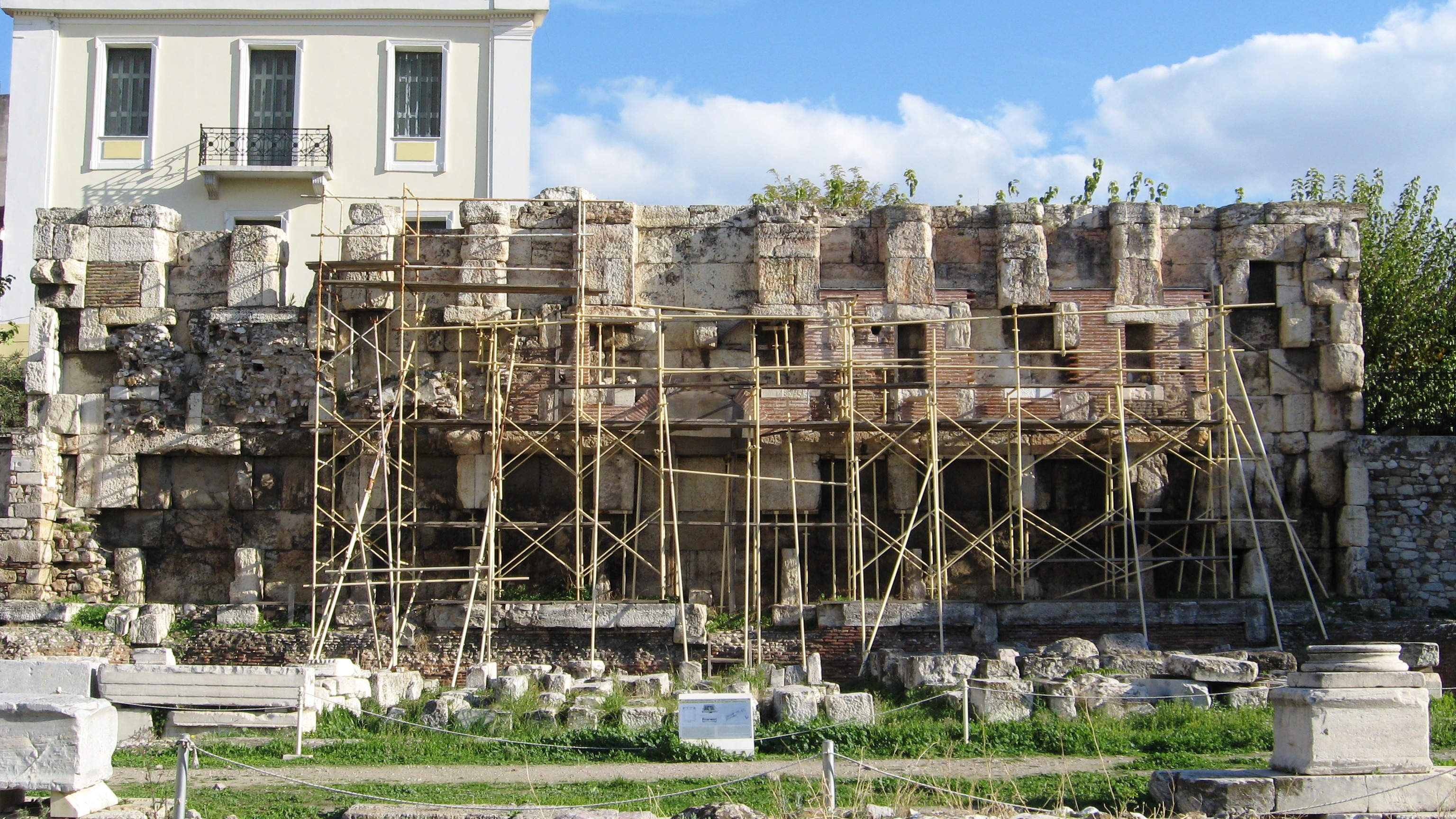
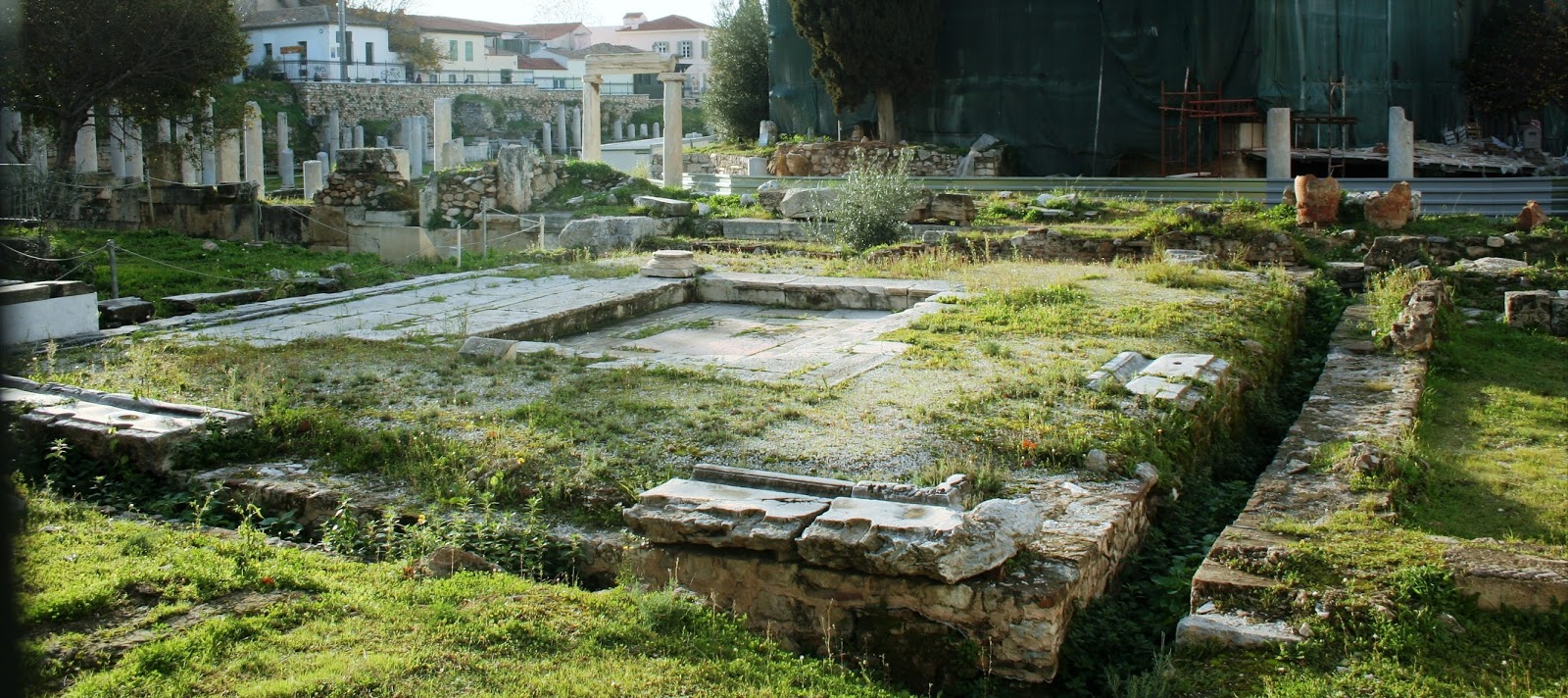




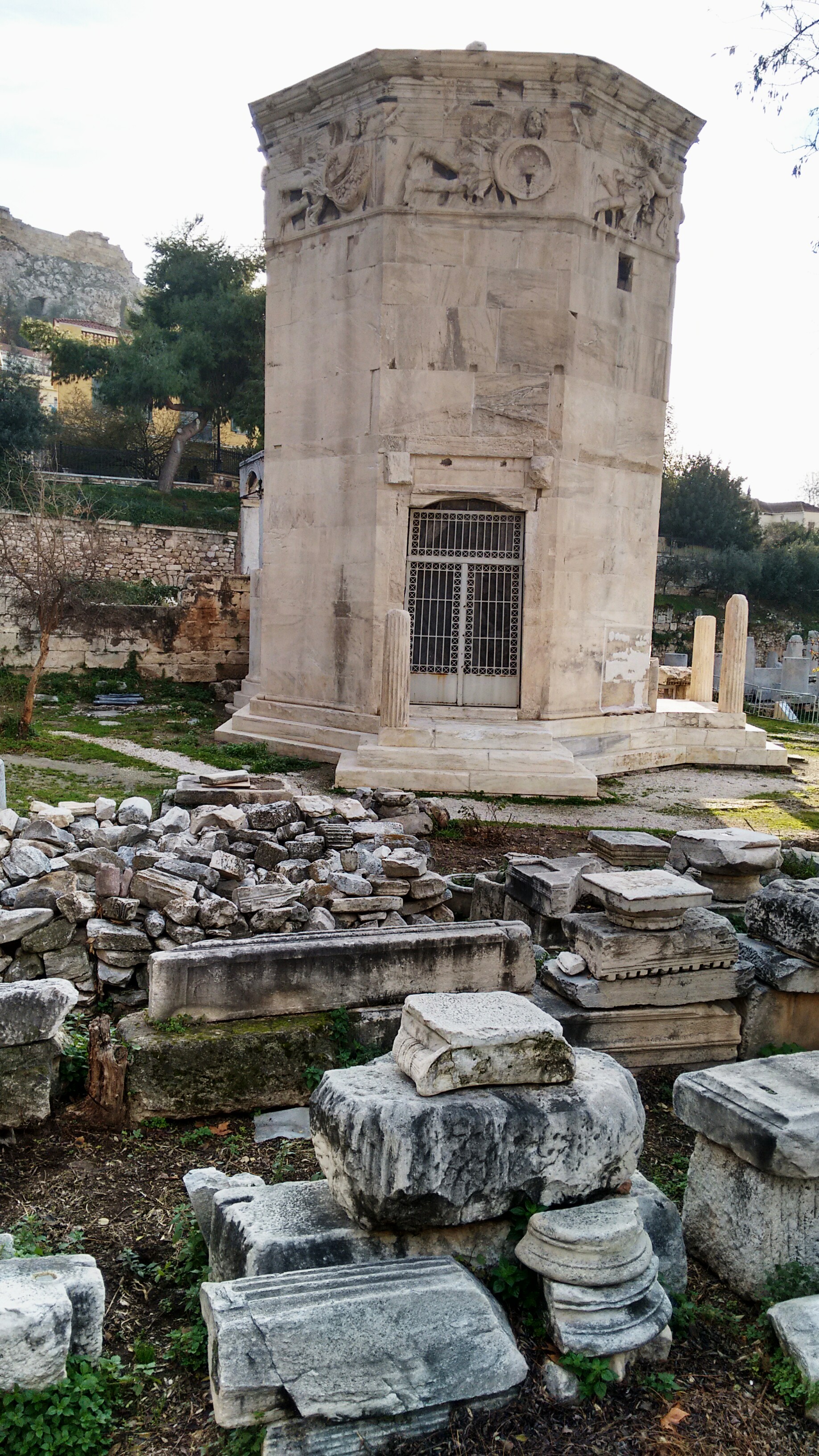
 One of the key buildings in the Roman Agora of Athens, which continues to impress tourists on the north side of the Acropolis, is the Tower of the Winds. As with the other buildings in Athens, it was built of that familiar Pentelic marble into a twelve-meter high clock tower. The building had just been restored with the scaffolding removed before I arrived, which was excellent timing to see a very ornate and beautiful ‘horologion’, or timepiece.
One of the key buildings in the Roman Agora of Athens, which continues to impress tourists on the north side of the Acropolis, is the Tower of the Winds. As with the other buildings in Athens, it was built of that familiar Pentelic marble into a twelve-meter high clock tower. The building had just been restored with the scaffolding removed before I arrived, which was excellent timing to see a very ornate and beautiful ‘horologion’, or timepiece.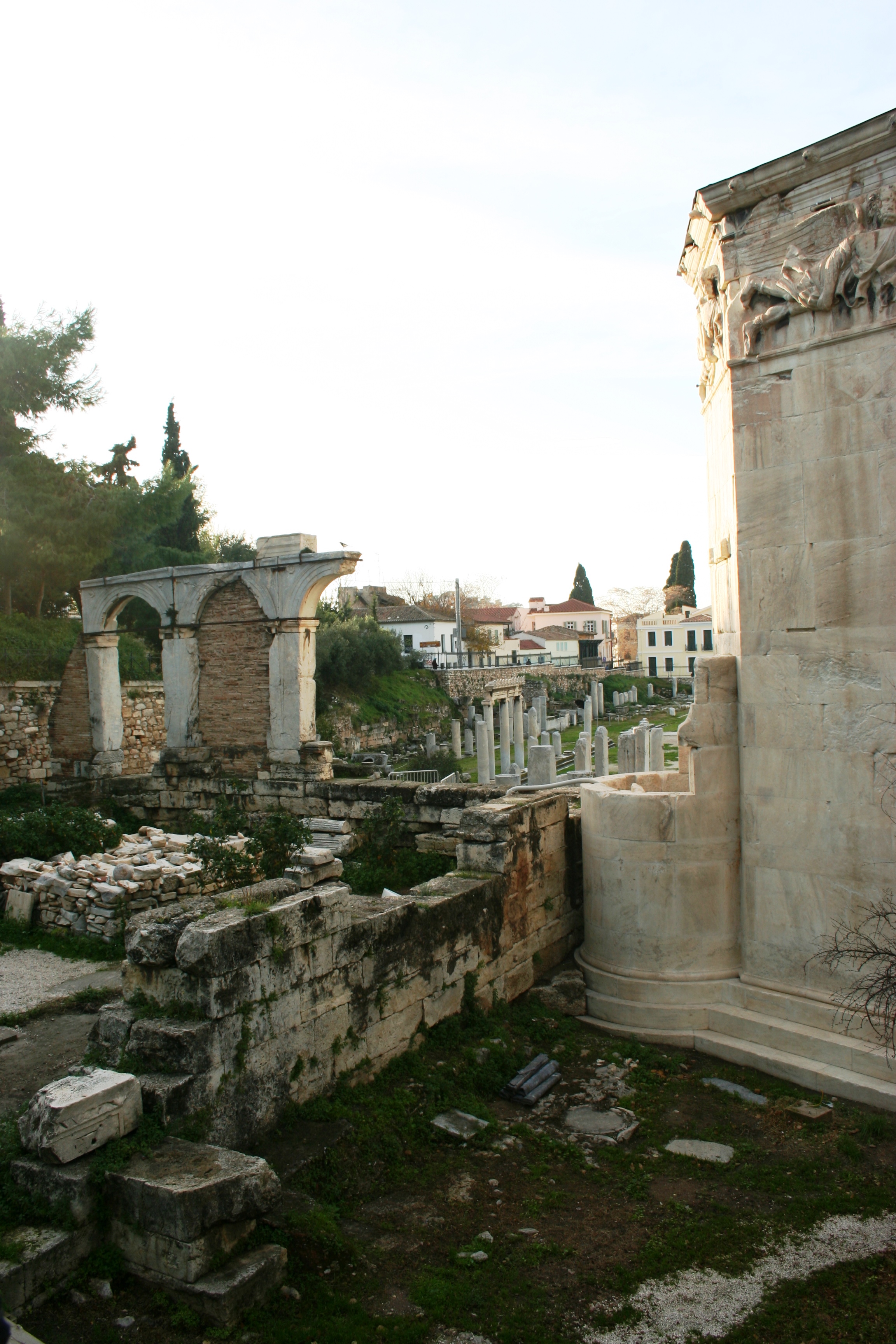
 The Roman Agora shows another product of the Italic investment in the city of Athens. Marking the entrance to the west of the Agora, it bears a dedication to ‘Athena the Originator’, not unlike the other monuments in Athens. However, the Roman gifted through the generosity of Julius Caesar and his son, the Emperor Caesar Augustus.
The Roman Agora shows another product of the Italic investment in the city of Athens. Marking the entrance to the west of the Agora, it bears a dedication to ‘Athena the Originator’, not unlike the other monuments in Athens. However, the Roman gifted through the generosity of Julius Caesar and his son, the Emperor Caesar Augustus.

 The Antigonid’s took over leadership of Macedon and Greece following the end of Alexander the Great’s family line, and successfully wielded the same ideology to justify their control over the Greeks: ‘protectors of Greek freedom’, an iron fist in a velvet glove so to speak; they controlled Greece through benevolent subjugation. Through the general practice of eugaritism (benefaction for honours), the Greeks were given beautiful buildings, festivals, and money in return for obeisance to Macedonian authority. For their own part, the Greeks had spent the last few hundred years restlessly under the yoke of the Macedonians, who they considered barely civilized.
The Antigonid’s took over leadership of Macedon and Greece following the end of Alexander the Great’s family line, and successfully wielded the same ideology to justify their control over the Greeks: ‘protectors of Greek freedom’, an iron fist in a velvet glove so to speak; they controlled Greece through benevolent subjugation. Through the general practice of eugaritism (benefaction for honours), the Greeks were given beautiful buildings, festivals, and money in return for obeisance to Macedonian authority. For their own part, the Greeks had spent the last few hundred years restlessly under the yoke of the Macedonians, who they considered barely civilized.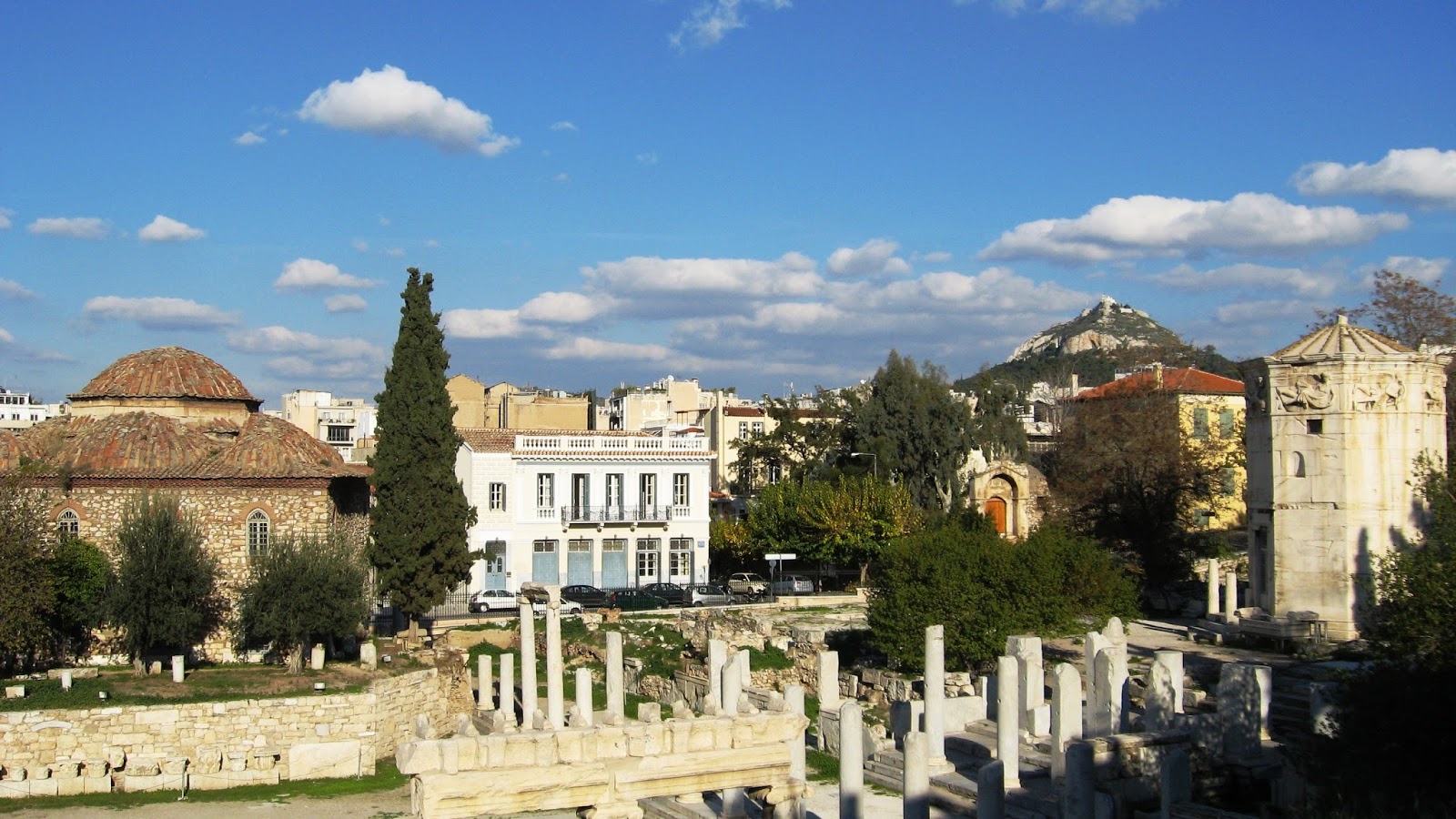
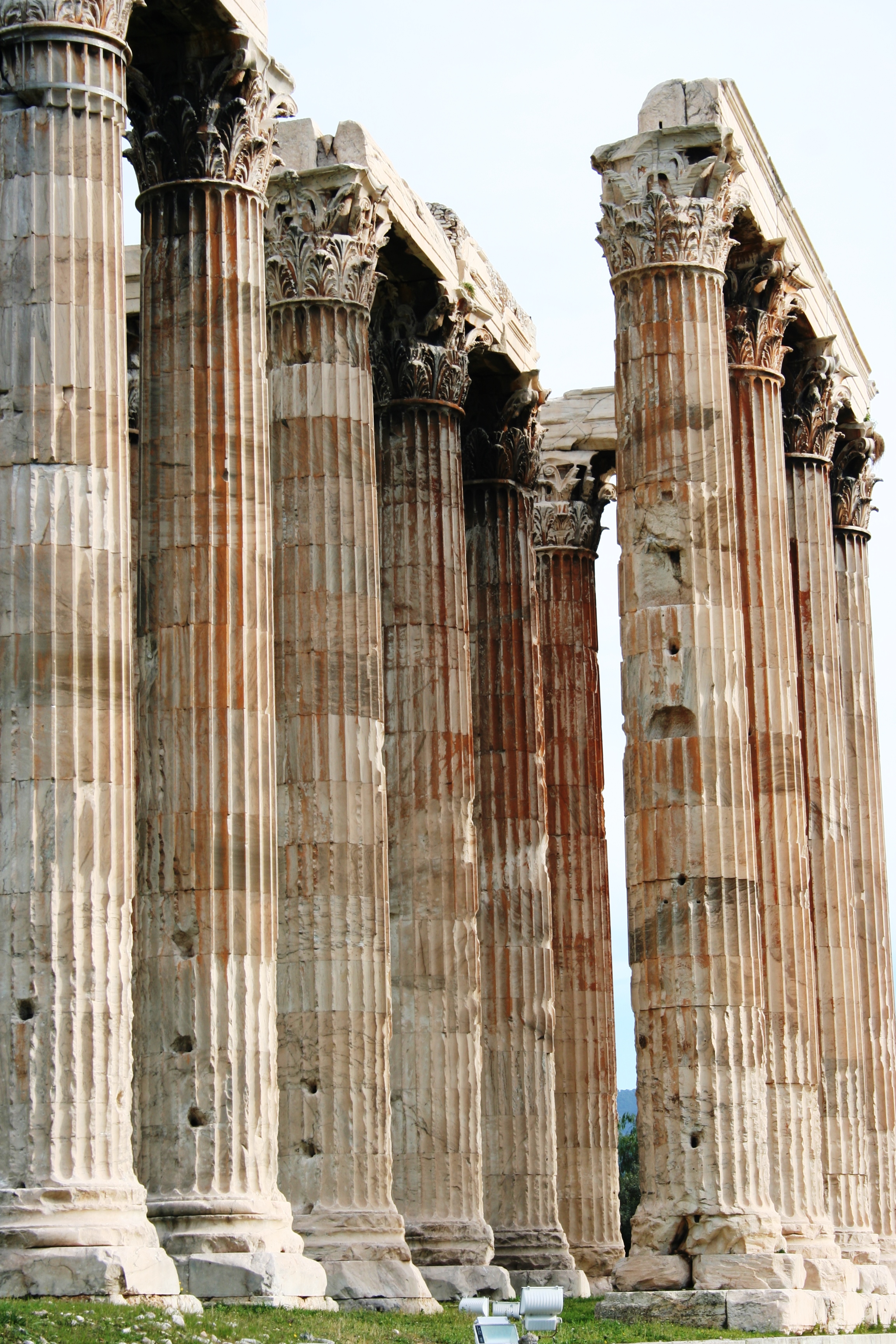
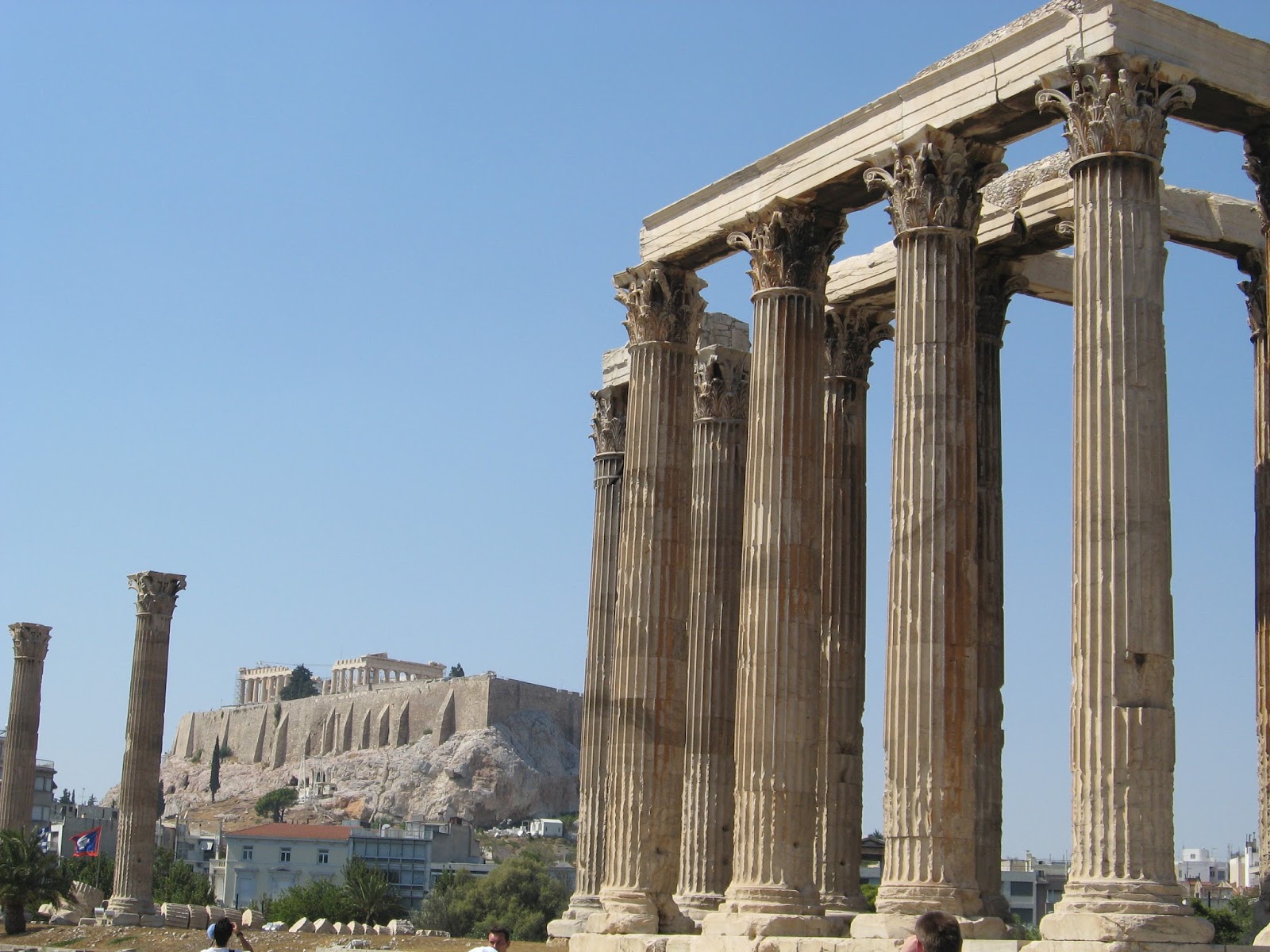
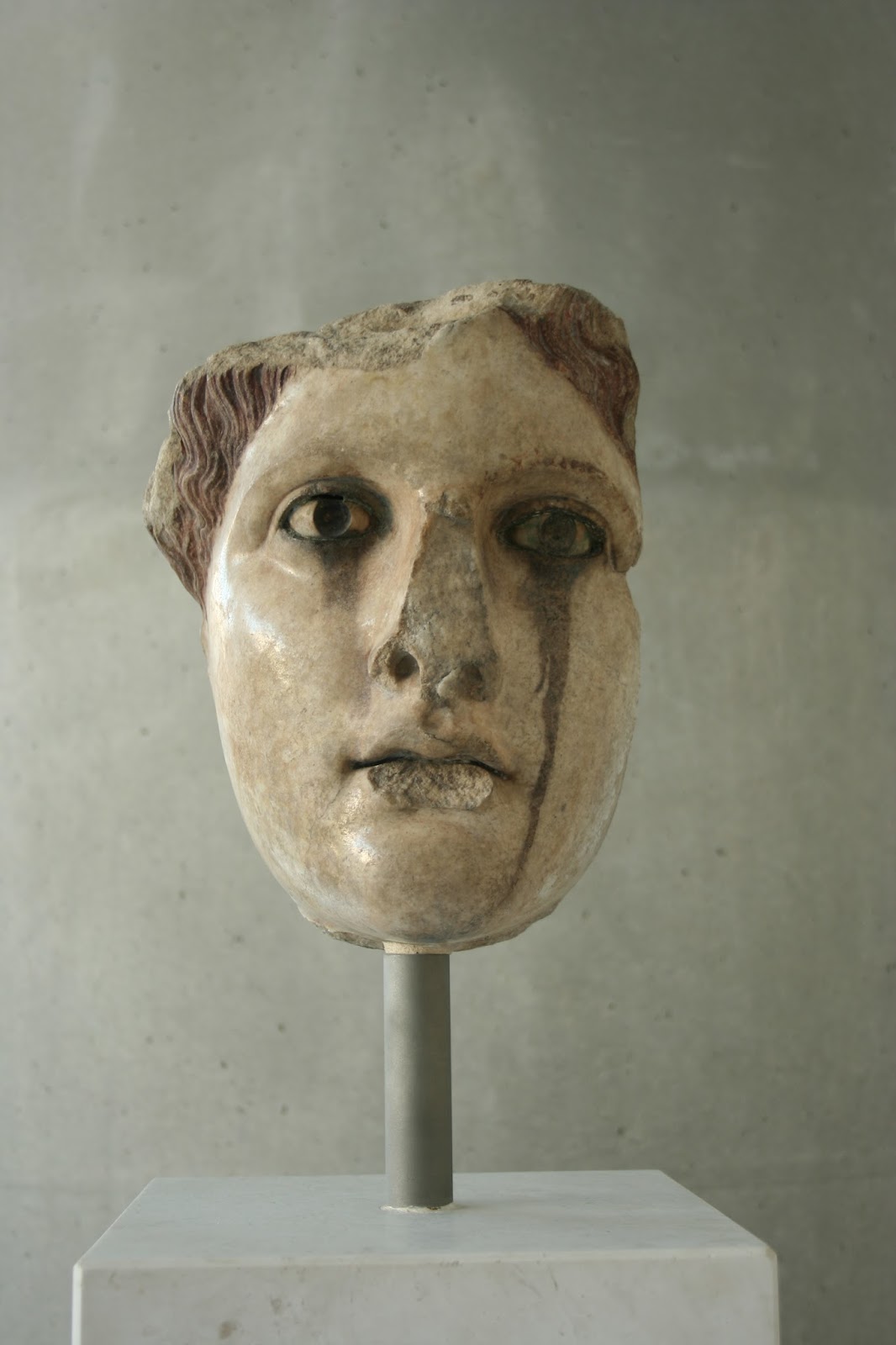






 What is the Hellenistic Period?
What is the Hellenistic Period?
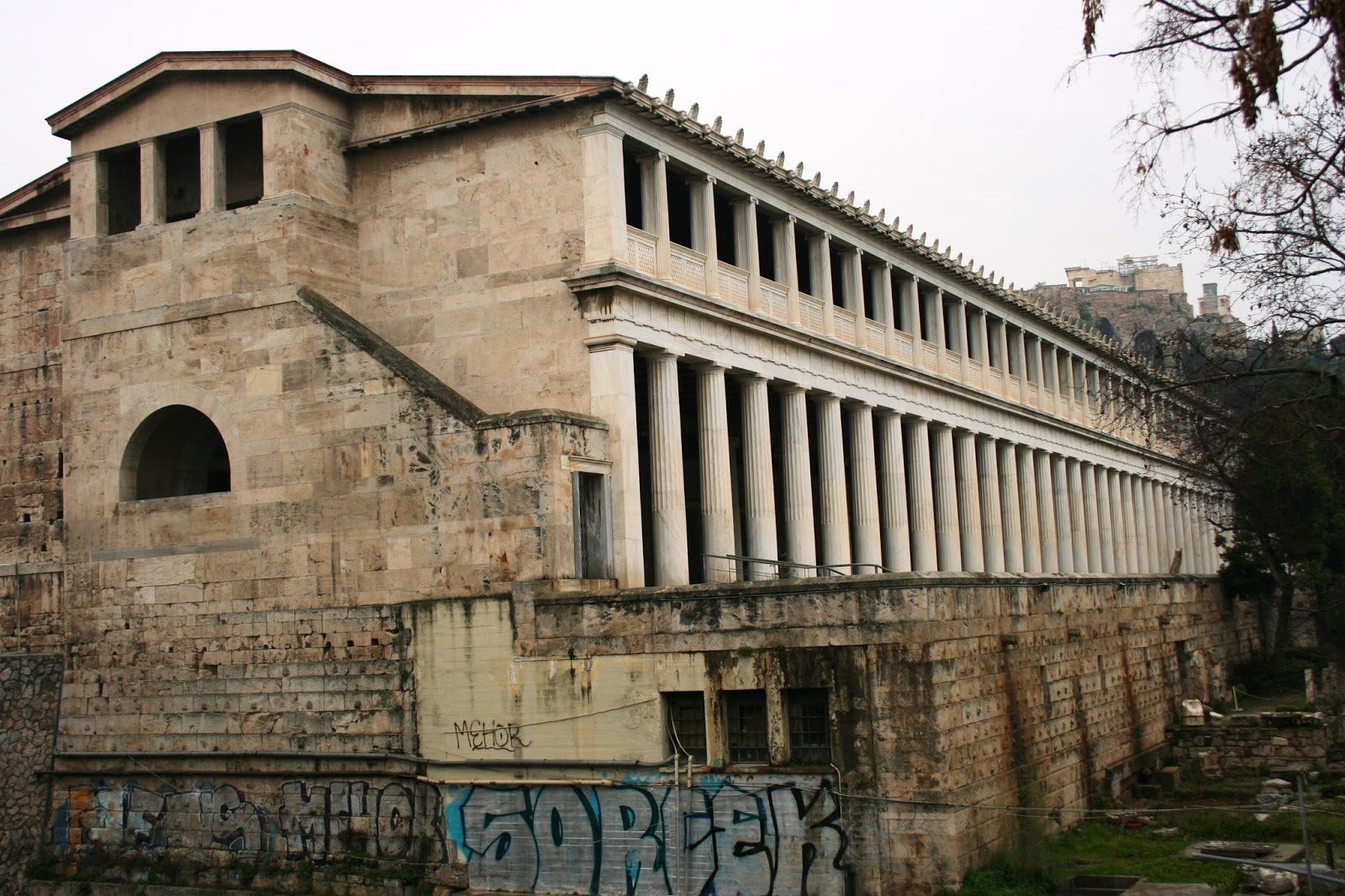
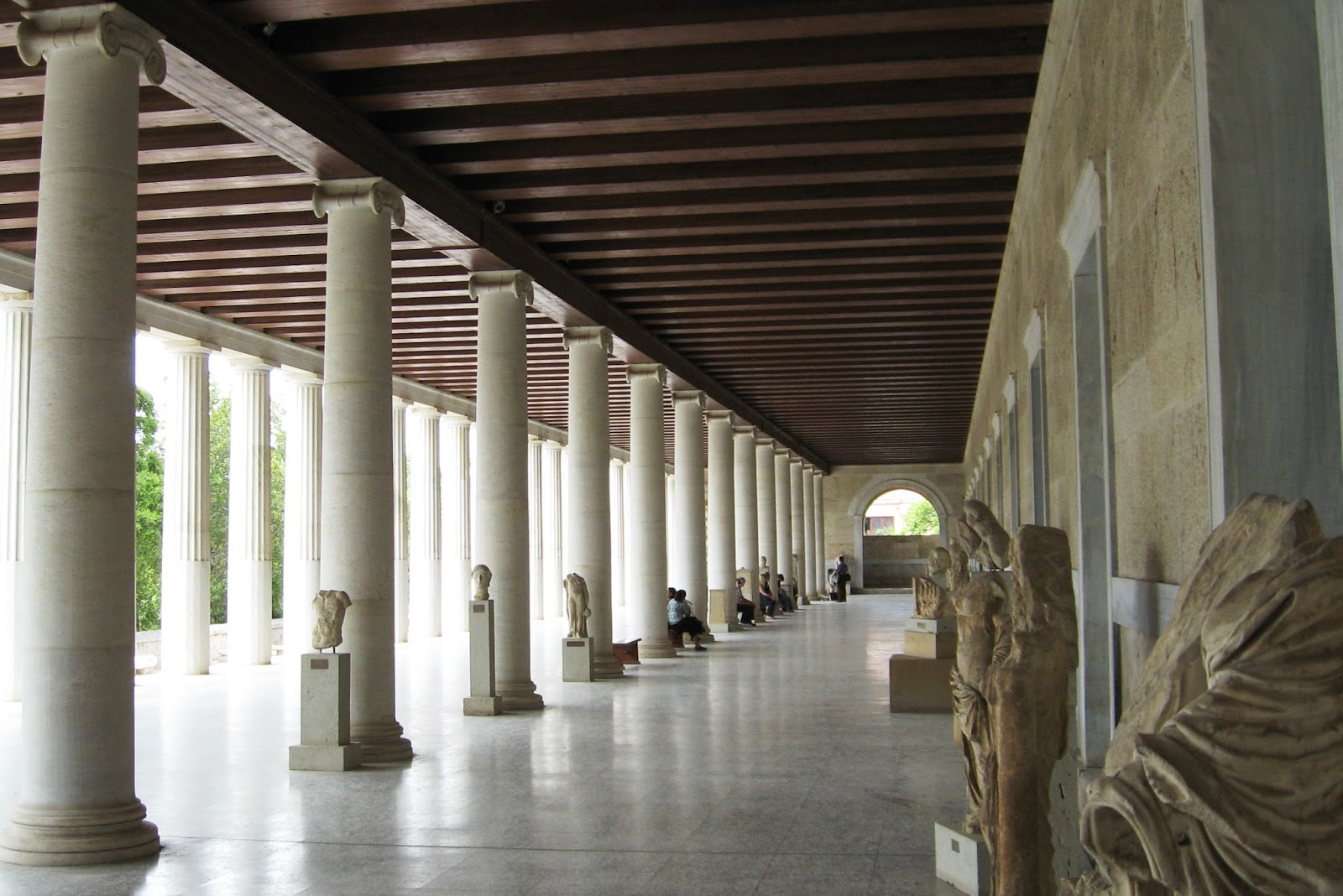





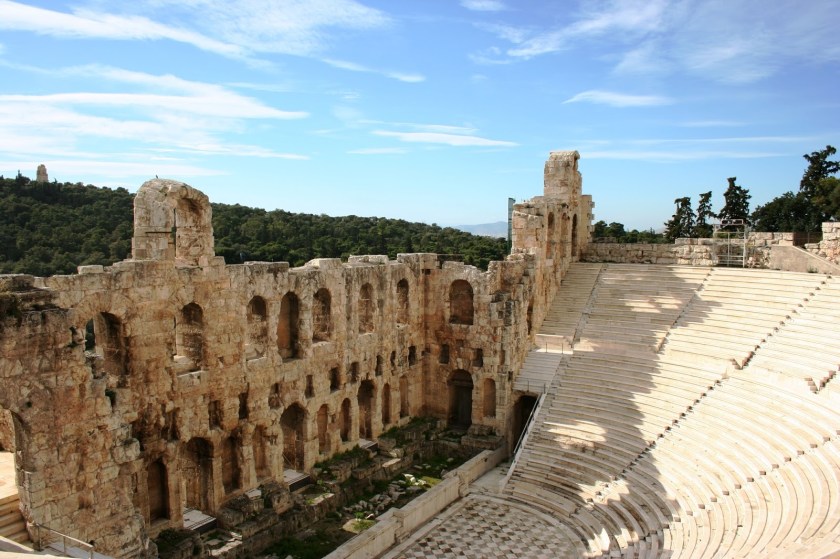
 Considered to be the first theatre in the world, it was used to honour the god of wine, revelry and theatre, Dionysus. Prior to anyone getting on with the show, a jaunty sacrifice of a bull was needed to kick off proceedings and purify the theatre. The festival of the Dionysia was celebrated here, with some of the biggest names in Classical literature of the age: Sophocles, Euripides, Aristophanes and Aeschylus.
Considered to be the first theatre in the world, it was used to honour the god of wine, revelry and theatre, Dionysus. Prior to anyone getting on with the show, a jaunty sacrifice of a bull was needed to kick off proceedings and purify the theatre. The festival of the Dionysia was celebrated here, with some of the biggest names in Classical literature of the age: Sophocles, Euripides, Aristophanes and Aeschylus. There were several phases of the Theatre of Dionysus, commencing with wooden seating in the 6th century BCE. The theatre is currently in pretty rough shape, though reconstruction work was completed between 2009 – 2015. The main problem, as with most buildings from antiquity, was that much of the stone was pilfered and used in other buildings nearby, or possibly carried off to be burned down in lime kilns.
There were several phases of the Theatre of Dionysus, commencing with wooden seating in the 6th century BCE. The theatre is currently in pretty rough shape, though reconstruction work was completed between 2009 – 2015. The main problem, as with most buildings from antiquity, was that much of the stone was pilfered and used in other buildings nearby, or possibly carried off to be burned down in lime kilns.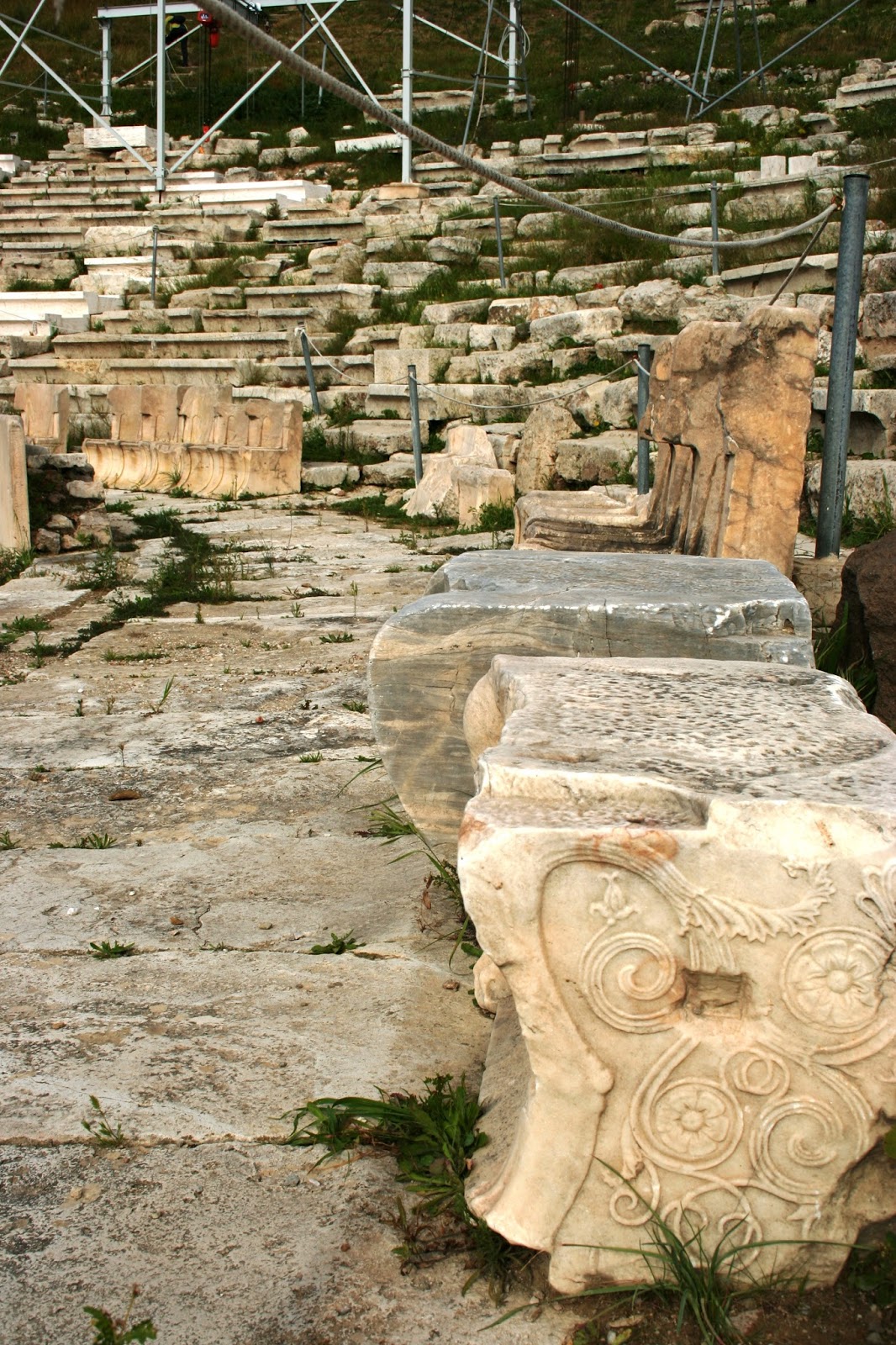
 Rather than making the riskier financial decision to invest in the support of new plays, which perhaps cut too closely to home (really reflecting the loss of autonomy felt by Greeks), instead the attention was focused on a golden age where their independence was trumpeted and powerful.
Rather than making the riskier financial decision to invest in the support of new plays, which perhaps cut too closely to home (really reflecting the loss of autonomy felt by Greeks), instead the attention was focused on a golden age where their independence was trumpeted and powerful. Awarded to the choregos, who was responsible for the training and sponsoring of the chorus in dramatic contests held in the Dinonysia, this is the only existing example of remaining in Athens today. Sculptures like this, would have been crowned with a bronze tripod which no longer survives. The limestone podium is topped with a cylindrical tholos of Pentelic marble, and six Corinthian columns which are topped by eight acanthus leaves.
Awarded to the choregos, who was responsible for the training and sponsoring of the chorus in dramatic contests held in the Dinonysia, this is the only existing example of remaining in Athens today. Sculptures like this, would have been crowned with a bronze tripod which no longer survives. The limestone podium is topped with a cylindrical tholos of Pentelic marble, and six Corinthian columns which are topped by eight acanthus leaves.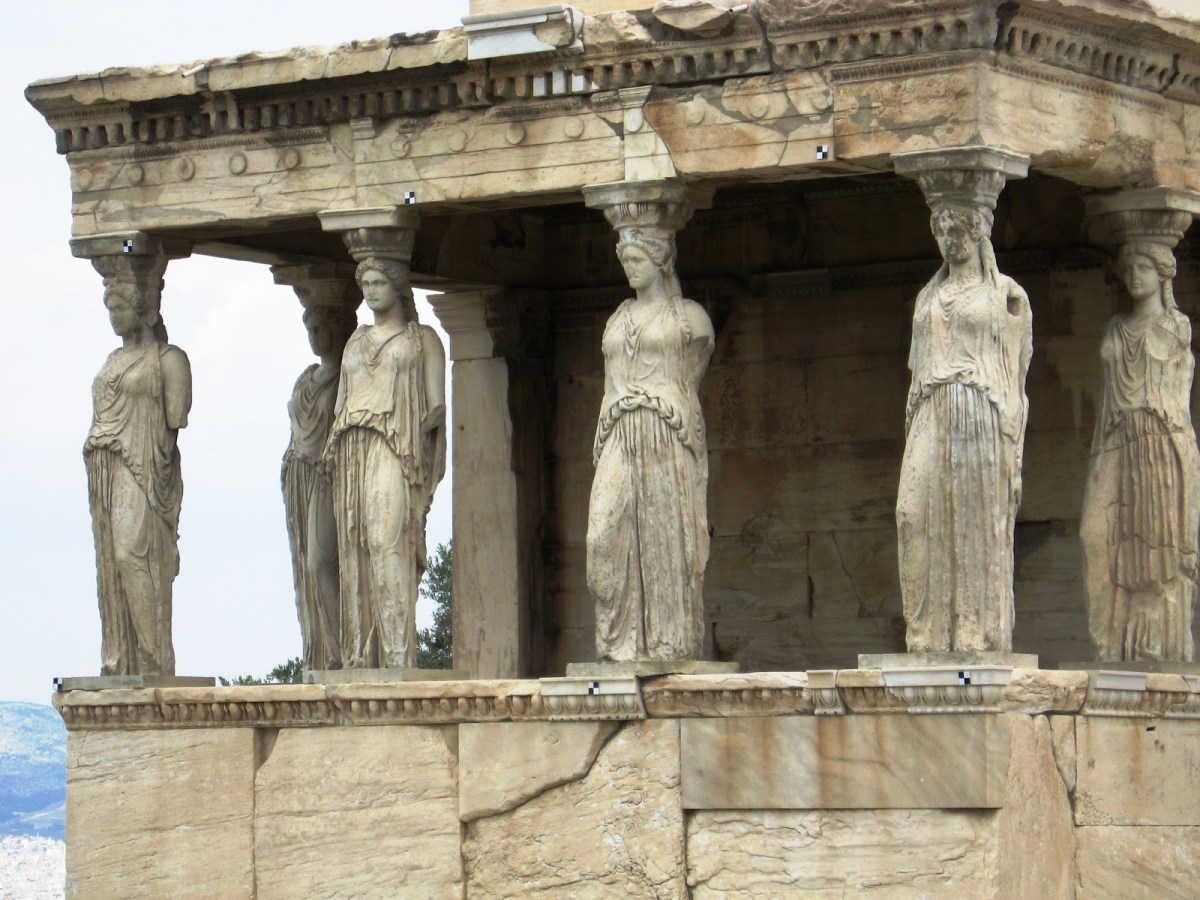
 The story of the Erechtheion was one of constant change. Built to replace the Old Temple of Athena, though not atop its foundations, it accommodated several cults in the same space. The building’s namesake was the hero and foster-child of Athena, Erechtheus. The temple was also dedicated to Athena, Poseidon, Hephaistos, and the hero Boutes – all worshiped in the same space.
The story of the Erechtheion was one of constant change. Built to replace the Old Temple of Athena, though not atop its foundations, it accommodated several cults in the same space. The building’s namesake was the hero and foster-child of Athena, Erechtheus. The temple was also dedicated to Athena, Poseidon, Hephaistos, and the hero Boutes – all worshiped in the same space. This temple offers an interesting glimpse at what was going on in Athens as it was building an empire. Pericles and other elites of Athensbrought together a mixture of local spaces routed heavily in the foundation mythology of the city and it’s heroes, and built up expensive, impressive buildings around them.
This temple offers an interesting glimpse at what was going on in Athens as it was building an empire. Pericles and other elites of Athensbrought together a mixture of local spaces routed heavily in the foundation mythology of the city and it’s heroes, and built up expensive, impressive buildings around them. The temple is on a slope (as you can see above) which sees the west and north side three metreslower than the southeast portion of the temple.The building size was reduced as a result of the shortage in funds during the Peloponnesian War, and the Caryatids placement hid the change in design.
The temple is on a slope (as you can see above) which sees the west and north side three metreslower than the southeast portion of the temple.The building size was reduced as a result of the shortage in funds during the Peloponnesian War, and the Caryatids placement hid the change in design. 




You must be logged in to post a comment.